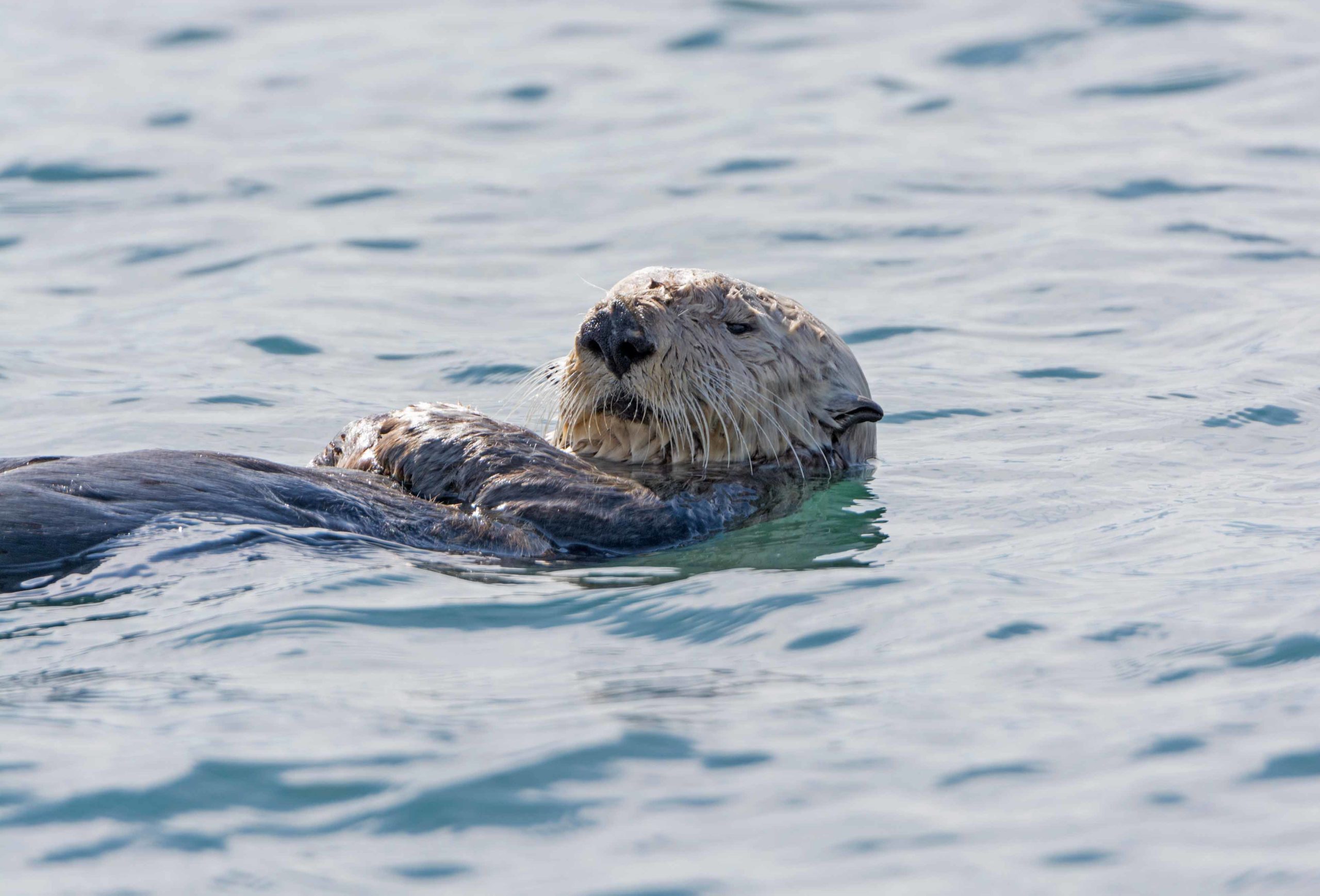
In the assessment, the Service concludes that a reintroduction of sea otters to their historical range in northern California and Oregon would provide substantial benefits to the species. As a keystone species, sea otters play a fundamental role in the ecological health of nearshore ecosystems. Sea otters eat sea urchins and other marine grazers, which helps keep kelp forests and seagrass beds in balance. Their presence in the ocean enhances biodiversity, increases carbon sequestration by kelp and seagrass, and makes the ecosystem more resilient to the effects of climate change. Additionally, reintroduction could increase the genetic diversity of recovering sea otter populations and contribute to the conservation of the threatened southern sea otter.